Explore our Climate and Energy Hub
23/06/2015
Governments are responsible for the majority of the delivery of education in Australia. The upcoming Federation White Paper will consider reducing or if appropriate, eliminating overlap between local, state and Commonwealth responsibility or involvement in the delivery and funding of public programs.
An appetite for integrated government has been demonstrated within Australia. One of the many issues to be considered include the principles and criteria to be applied when allocating roles and responsibilities between different levels of government such as equity, efficiency and effectiveness of service delivery, including a specific focus on service delivery to the regions.
Not all Australians benefit equally from these high quality services. The uneven distribution of services across Australia has important implications for those in less-favoured locations. What this means is that any changes to the structure of government schools is likely to have a disproportionate impact on regional Australia, as a higher percentage of students participate in government schools in regional areas compared to metropolitan areas, as shown in Figure 1.
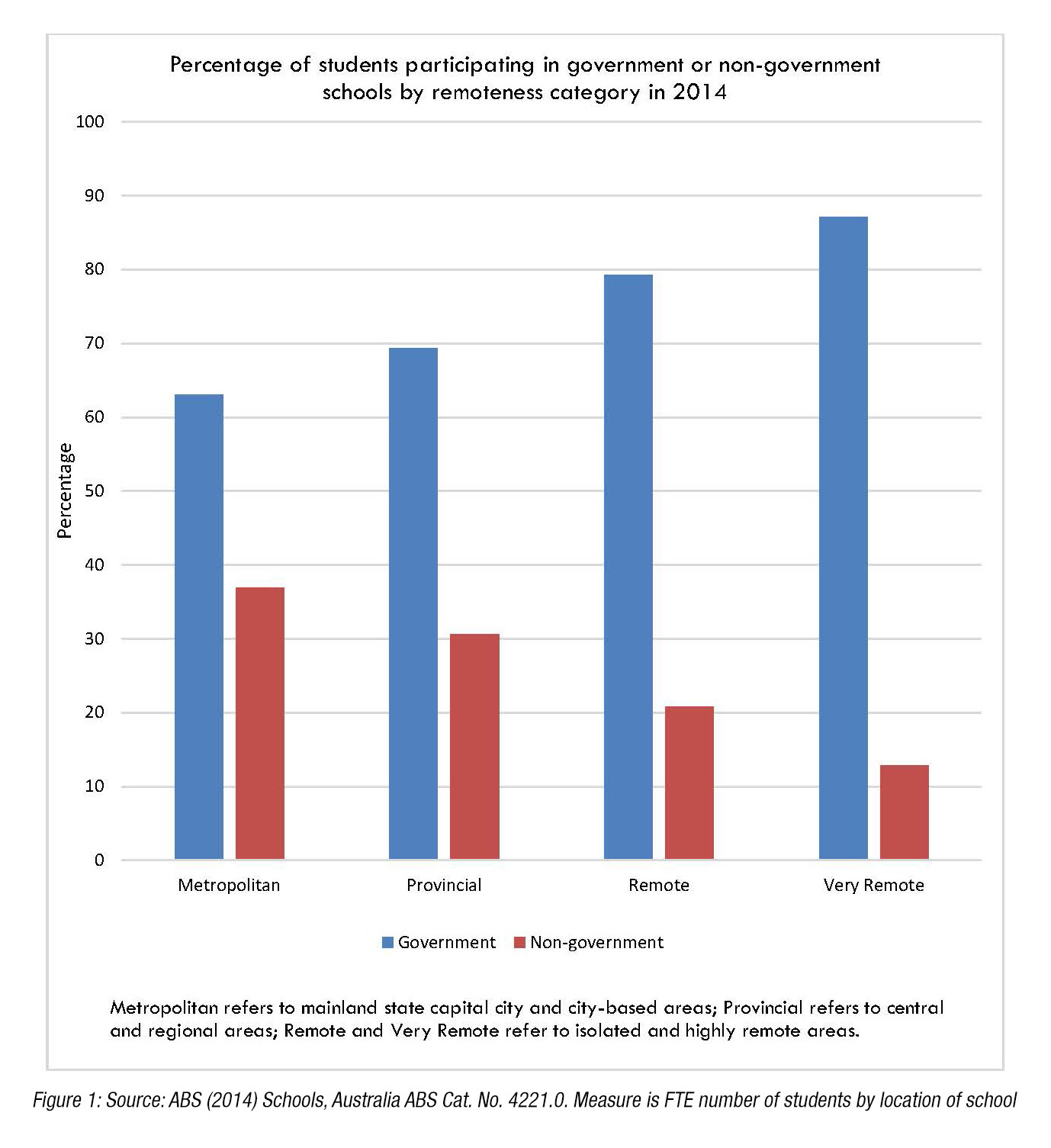
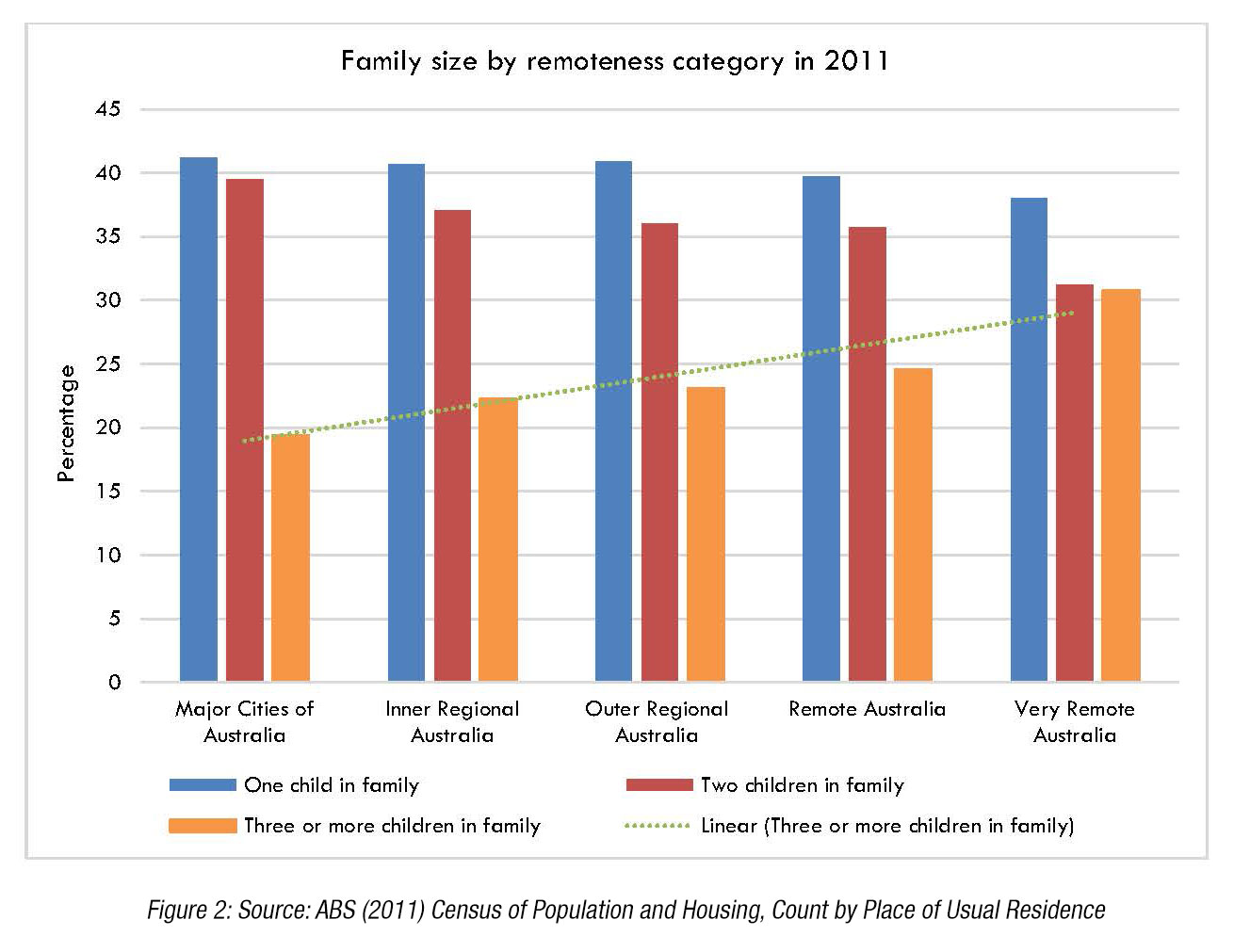
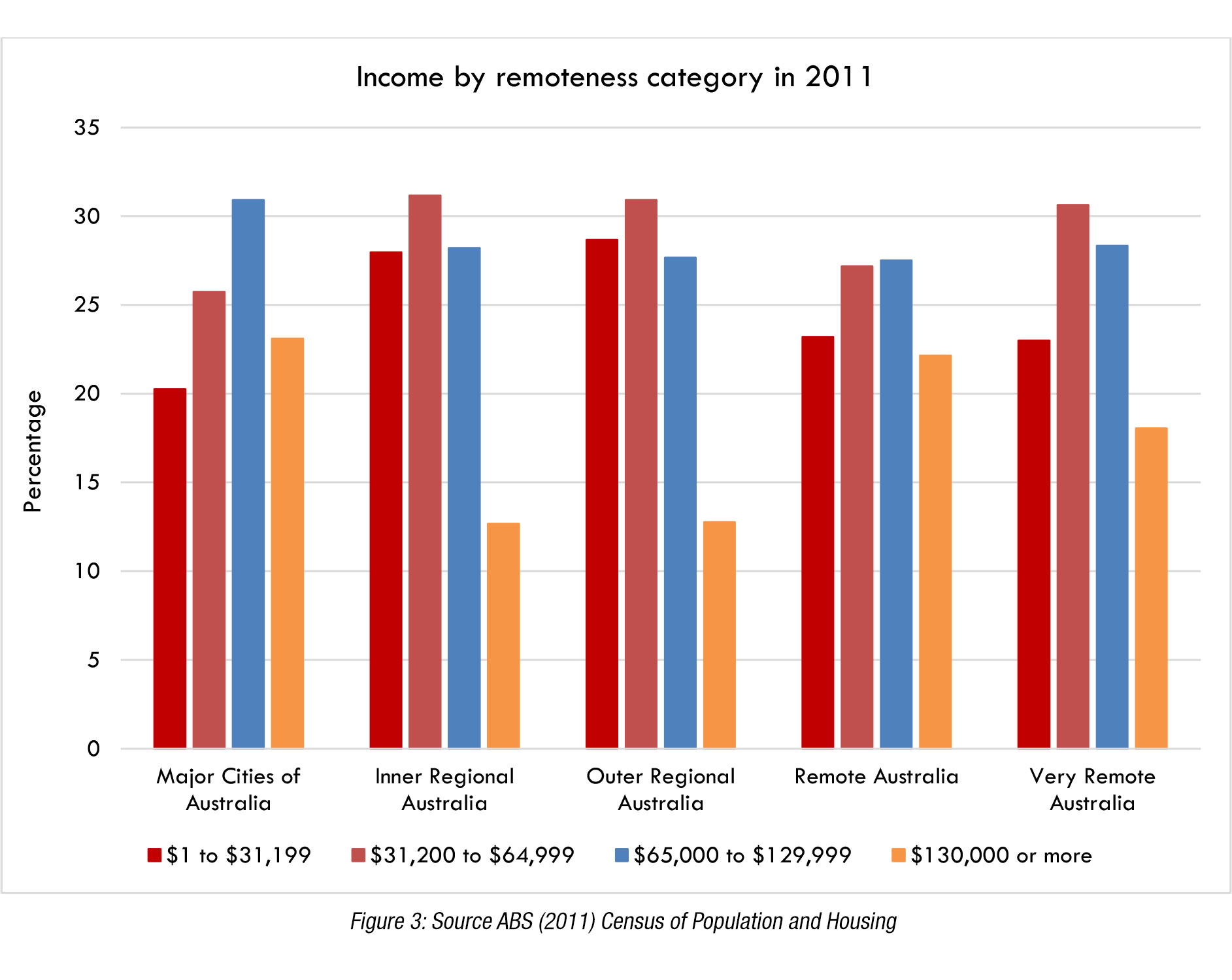
To emphasise this point, families in regional Australia tend to have larger families compared to families in metropolitan areas as shown in Figure 2, and those living in regional Australia are more likely to be in low income brackets and less likely to be in high income brackets than people in metropolitan areas (Figure 3).
There is now a strong case for examining how governments across Australia can better deliver services to regional Australia. Systemic changes are required in how we deliver services in regions so they can grow and prosper.
Effective governance for regions is a product of positive engagement between central governments and the regions; it is based on relationship building and the generation of new capacities in both the centre and the periphery and, it is outcomes focused.
In large measure, the answer to the challenge of creating better government for Australia’s regions will be a suite of policy measures rather than a single action or initiative. Any viable solution must involve both greater dialogue between the regions and central government and the transfer of power. Such ideas can be challenging, but are essential if regional Australia is to achieve its potential.
Skills acquisition presents a picture of divided responsibilities across the three tiers of government. Educational attainment and skills acquisition is a fundamental determinant of the wellbeing of regions. In Australia there is little local input into either the formal education system or the employment training system and, perhaps more importantly, provision is fractured across the three tiers of government, as well as the private sector.
All things being equal, regions with a better skilled and educated workforce will be more prosperous, resilient, healthy and adaptable to changing conditions. Regions across Australia, however, often report significant shortfalls in areas such as vocational training. This is largely because of factors unique to that set of locations such as small population size, a specialised economy and lack of interest from private financiers of infrastructure.
Commonly, vocational education is organised along industry, rather than geographic lines and while there may be concentrations of particular industries in defined localities, there is scant recognition of local governments and communities in the structure of the education system.
Regional input into national or state-based training plans is limited, and we can expect relatively limited flexibility in the delivery of programs in either policy domain. The complexity of the challenges warrants the need for a more nuanced approach to all policy. Cumulative and isolated decisions are likely to continue to result in duplication, further disadvantage and greater complexity for policy makers and regions.
Concentration on policy clearly marked ‘regional’ will not be enough to meet the challenges facing regions. A joined-up approach is what we need.
Su McCluskey participated in CEDA's State of the Nation conference, click here to watch videos.
